April is a time to raise awareness about the importance of oral cancer screenings. Your Southcoast primary care provider or a dentist can screen you during regular visits. Oral cancer is fairly common and can often be cured if found and treated in the early stages. It is important to tell your doctor or dentist right away about any problems you have in your mouth or throat.
What is Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer is a type of head and neck cancer that typically starts in cells in the mouth or throat. Oral cancer can affect how you chew, swallow, talk and can sometimes even affect breathing. Oral cancer is fairly common and can often be cured if found and treated in the early stages.
A doctor or dentist can often detect oral cancer in its early stages because the mouth is easy to examine.
Types of Oral Cancer
More than 9 in 10 oral cavity tumors are squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cells make up the lining of the oral cavity (the mucosa). As cancer in the mouth’s lining grows, it can spread into nearby tissues.
Verrucous carcinoma is a rare type of squamous cell carcinoma. It’s a low-grade or slow-growing type that rarely spreads to distant sites (metastasizes). It accounts for less than 1 in 50 oral cancers.
Other much less common oral cancer types include salivary gland tumors, including adenoid cystic carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, mucoepidermoid, and lymphoma.
Understanding the Mouth and Throat
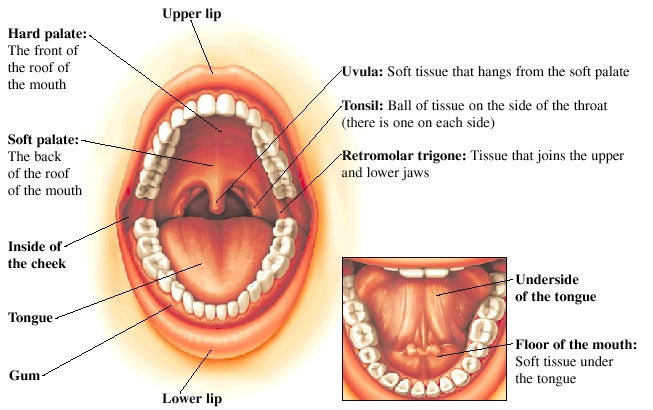
Every part of the mouth has an important function. For instance, the lips are needed to speak. The tongue is also key to speaking and swallowing. The gums help protect the teeth and keep them healthy.
The mouth is also called the oral cavity. It includes many parts:
- The lips
- The lining inside the lips and cheeks (called the buccal mucosa)
- The front two-thirds of the tongue
- The gums and teeth
- The bottom (or floor) of the mouth
- The bony top of the mouth (hard palate)
- The area behind the wisdom teeth (retromolar trigone)
Symptoms
Oral cancer is often found because a person notices abnormal changes in their mouth. You can check your mouth for early signs of oral cancer. All you need to do is look at your mouth in a mirror. Look for:
- A sore on your lip or in your mouth that won’t heal
- A lump or thickening on your lip, in your mouth, or in your throat
- A white or red patch on your gums, tongue, or the lining of your mouth
Other symptoms include:
- Abnormal bleeding, pain, or numbness in your mouth
- A feeling of something caught in your throat
- Trouble or pain when moving your tongue, chewing, or swallowing
- Loose dentures or changes in the way they fit
- Swelling around your jaw
- Loose or painful teeth
- A lump, swelling, or mass in your neck that doesn’t go away
- A change in your voice
Only a healthcare provider can tell if you have cancer. Tell your doctor or dentist right away about any problems you have in your mouth or throat.
Preventing Oral Cancer
The best way to protect yourself from oral cancer is to know your risk factors. You can’t change some risk factors, but others you can prevent or change with lifestyle modifications.
To help prevent oral cancer:
- Don’t use any form or type of tobacco.
- Stay away from other people’s smoke (secondhand smoke)
- Limit how much alcohol you drink or don’t drink at all
- Protect yourself from UV light exposure. People who spend a lot of time in the sun have a greater risk for lip cancer. Protect your lips with sunscreen or lip balm with an SPF of 30.
- Prevent HPV infection. Limit your risk for oral human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. The risk for HPV is higher in people who have oral sex and multiple sex partners. The HPV vaccine might help lower the risk of these cancers.
- Eat well. People with poor diets have a greater risk for these cancers. It’s important to eat a healthy diet focused on plant-based foods.
- Have your dentures correctly fitted. Dentures that rub the inside of the cheeks or the tongue can cause irritation that changes the cells of the mouth. This may lead to an increased risk for cancer over time. All denture wearers should remove and clean their dentures every night and have them regularly checked by a dentist. Everyone should get regular dental care.
Risk Factors: Cancer and Tobacco
- Tobacco use is a major risk factor for lung, mouth, throat, bladder, and many other cancers. In fact, smoking is the cause of cancer in 1 out of 5 people diagnosed in the U.S.
All tobacco products, including cigarettes, cigars, pipe tobacco, chewing tobacco, and snuff, contain the following:
- Poisonous substances (toxins), like cyanide, lead, and arsenic
- Known cancer-causing agents called carcinogens (There are at least 70 carcinogens in tobacco smoke.)
- Nicotine, an addictive substance
- For more information and tips on how to quit, please visit: Cancer and Tobacco (southcoast.org)
Additional Risk Factors
- Drinking alcohol in large amounts over a long period of time
- The risk for oral cancer is even higher in people who use both tobacco and alcohol.
- HPV infection
- Sun exposure (ultraviolet radiation) can cause lip cancer
Oral Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment in MA and RI
At Southcoast Health, we strive to keep our surrounding communities in Massachusetts and Rhode Island informed and proactive about their health.
If you’re at risk for oral cancer, making lifestyle changes can help prevent or reduce your chances of developing cancer. We know making changes can be hard, but your healthcare provider can suggest resources and provide support.
We also stress the importance of proper screening, so if you are experiencing symptoms that concern you, please make an appointment today.
Early detection can lead to a cure when it comes to oral cancer, so please don’t hesitate to contact your primary care provider at Southcoast Health today to stay on top of your mouth and throat health.
